Geriatric Trauma Centre

In a geriatric trauma centre (ATZ), elderly patients are treated holistically with an interdisciplinary concept of traumatology, geriatrics, and other specialties. Stringent specifications and comprehensive quality requirements of the German Society for Trauma Surgery (DGU) are met and regularly verified in audits.

Preventing a fracture from becoming a burden
The fracture that surgeons treat is usually not the patient's underlying problem, but rather the causes that led to the fall. Incipient dementia or progressive loss of vision, balance and coordination are possible internal causes resulting in falls. A fall resulting in injury indicates the particularly increased vulnerability of the geriatric patient, which is referred to as "frailty". The decisive task of a geriatric trauma centre is to recognise this and to carefully accompany patients who are particularly at risk throughout their hospital stay.
A fall rarely comes alone
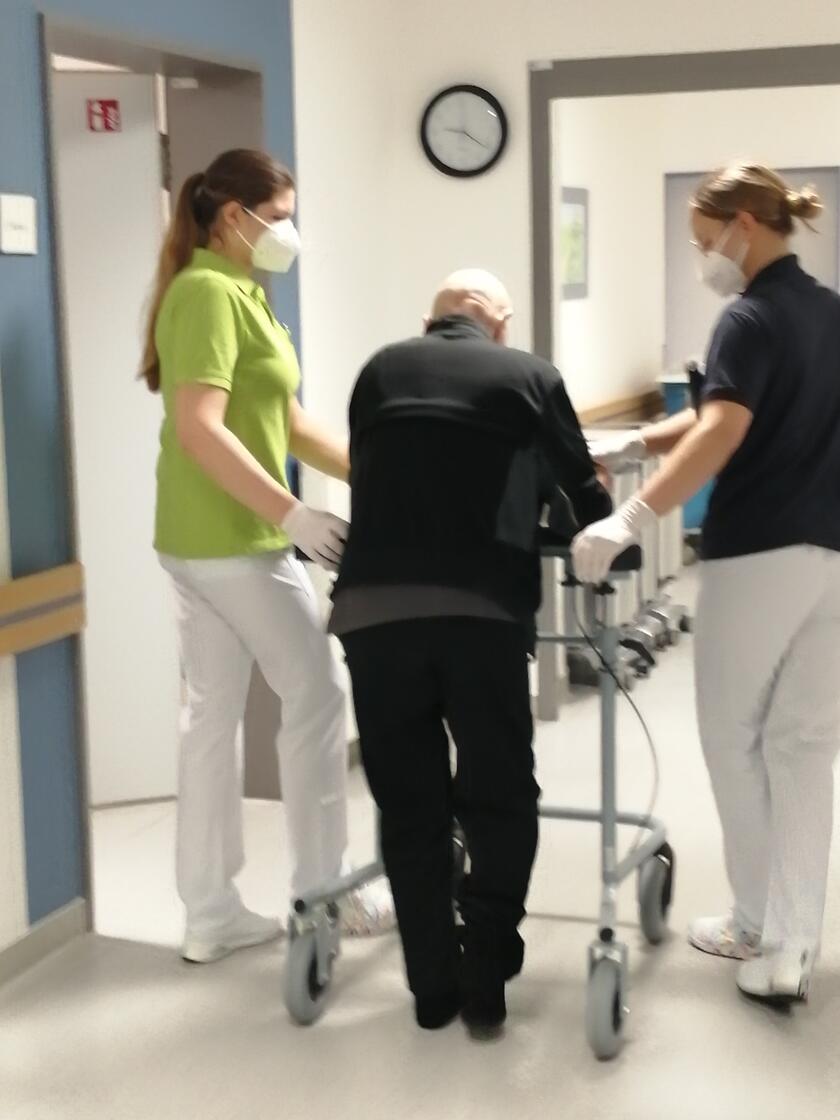
For the patient, this means optimised fracture care and individually tailored structured rehabilitation treatment. Our staffs many years of experience and the high level of competence in the treatment of elderly and frail people are also important here. The ATZ not only examines an organ, but also the person as a whole with their fears, wishes, goals and values.
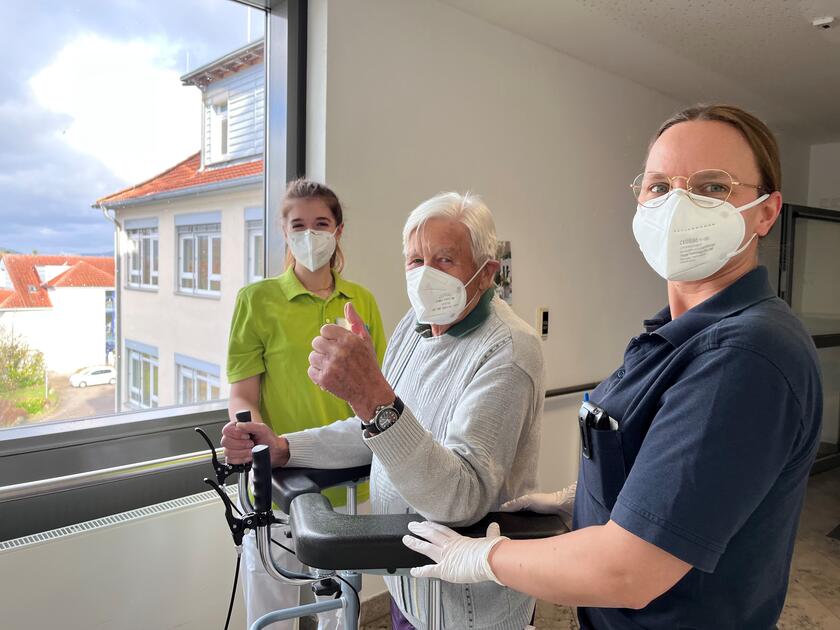

Interdisciplinary work is required
The cooperation of a wide variety of professional groups is a prerequisite for the therapeutic approach, which consequently often leads to early complex rehabilitation treatment. Specialists in geriatrics and trauma surgery provide individual care for the patient together with specialist nurses, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, and speech therapists.
Our services
- Combined competencies of trauma surgery and orthopaedics with geriatrics
- Recording of the exact cause of the fall, concomitant diseases, cognitive and motor skills, memory and arithmetic abilities, possible balance problems, and hearing and vision.
- Bone fractures, open fractures, leg fracture, odontoid (dens) fracture, humerus head fracture, lumbar vertebral fracture, humerus fracture, femur fracture, femur neck fracture, pathological fracture, periprosthetic fracture, tibia fracture, vertebral fracture
- Endoprosthesis, hip replacement, reverse shoulder replacement, artificial hip, artificial hip joint, artificial knee, artificial knee joint, artificial shoulder joint
- Interdisciplinary care by specialists in traumatology and specialists in geriatrics, as well as the participation of all necessary professions (specialized nursing, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy and neuropsychology).
- If indicated, direct transfer to geriatric complex treatment
- Acute geriatrics
- Senile dementia/Alzheimer's dementia/Alzheimer's symptoms/Alzheimer's test/onset dementia/Dementia symptoms/Dementia test/management of dementia/vascular dementia/ symptoms
- Alzheimer's disease/morbus Parkinson
- Parkinson's Disease/Syndrome/Symptoms/Parkinson's Dementia/Parkinson's Diagnosis
- Osteoporosis Treatment/Diagnosis/Therapies/Nutrition in Osteoporosis
- Osteopenia
- Regular evaluation of the patient’s development through an interdisciplinary approach.
- Participation in the geriatric trauma register
