Bone fractures
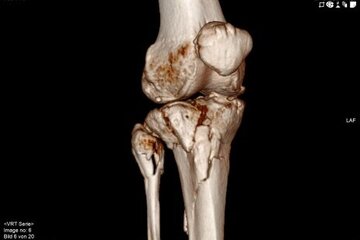
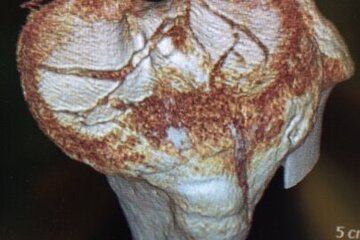
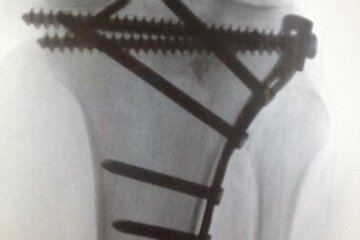
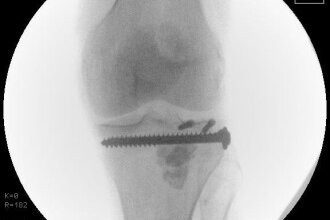
Bone fractures of the tibial plateau or knee joint are rare injuries; the incidence of tibial plateau fractures is only about 10/100,000 per year. Young patients usually have a rasan trauma (accident). In older patients, however, even minor injuries, e.g. twisting of the ankle, can lead to serious injuries. These injuries to the knee joint - as they destroy the joint surface in the knee - mean an increased risk of suffering arthrosis (wear and tear of the joint). Patients also often do not regain their original sporting level. The aim of the operation is an almost anatomical restoration of the joint surface, the leg axis and, if necessary, the treatment of concomitant injuries in the joint. Open, minimally invasive, and arthroscopic surgical procedures are available to us for this purpose. The fractures are stabilised with various plate systems and/or free screws. An individual and fracture-specific surgical strategy is necessary for stabilisation. X-rays, computer tomography and, if necessary, magnetic resonance imaging help with the planning.